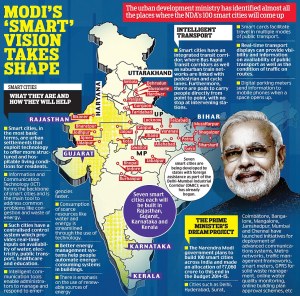
$$ The Cabinet recently cleared Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s favoured 100 smart cities project in a bid to recast the urban landscape of the country to make them more livable and inclusive besides driving economic growth.
$$ The 100 smart cities mission intends to promote adoption of smart solutions for efficient use of available assets, resources and infrastructure with the objective of enhancing the quality of urban life and providing a clean and sustainable environment.
$$ The Cabinet chaired by Modi approved central government spending of about rupees one lakh crore on urban development under two new urban missions over the next five years.
$$ the Smart Cities Mission will get an outlay of Rs 48,000 crore.( the AMRUT mission will received Rs 50,000 crore over the next five years. In comparison, the central outlay for nine years of the JNNURM mission was Rs 42,900 crore.)
$$ Under the Smart Cities Mission, each selected city would get central assistance of Rs 100 crore per year for five years.
$$ Under this mission, 10% of the budget allocation will be given to states/union territories as incentive based on achievement of reforms during the previous year
$$ “Efficiency and sustainability will be of major focus in the establishment of smart cities.
$$ Accountability will be the most important factor in fund disbursal to the states and it will based on the time bound completion of projects.
$$ Each Smart City aspirant will be selected through a ‘City Challenge Competition‘ intended to link financing with the ability of the cities to perform to achieve the mission objectives.
$$ “Each state will shortlist a certain number of smart city aspirants as per the norms to be indicated and they will prepare smart city proposals for further evaluation for extending central support,” said a statement from the ministry of urban development.
$$ Smart Cities Council India founder and President : mr. Pratap Padode.
1. What is a ‘smart city’?
A city equipped with basic infrastructure to give a decent quality of life, a clean and sustainable environment through application of some smart solutions.
2.Basic infrastructure
Assured water and electricity supply, sanitation and solid waste management, efficient urban mobility and public transport, robust IT connectivity, e-governance and citizen participation, safety and security of citizens.
3.Smart solutions
Public information, grievance redressal, electronic service delivery, citizens’ engagement, waste to energy & fuel, waste to compost, 100% treatment of waste water, smart meters & management, monitoring water quality, renewable source of energy, efficient energy and green building, smart parking, intelligent traffic management system.
4.What’s the next step?
The next step is identification of the 100 cities and for this a city challenge competition to be conducted by Bloomberg Philanthropies is envisaged. The current plan looks to select 20 cities this year followed by 40 each in the next two years.
5.Smart Cities Council India has been formed
It is part of the US-based Smart Cities Council, which is a consortium of smart city practitioners and experts, with a 100-plus member and advisor organizations operating in over 140 countries.
6.All states will get at least one smart city
A Special Purpose Vehicle will be created for each city to implement Smart City action plan. The SPV will be signed with the urban local body, state government and the Centre for implementation of the project.
7.How it will work
After government announces the guidelines, states will be asked to nominate names of cities for a ‘City Challenge Competition’ and the chosen ones will get Central fund of Rs 100 crore each year for 5 years.
8.The basic criteria for selection of a city/municipal area
9.Area-based development
1. Retrofitting 500 acres: Planning in an existing built-up area in a municipal ward, preparing plan with citizen participation (example: Connaught Place in Delhi, Bhendi Bazar in Mumbai).
2. Greenfield 250 acres: Introduce smart solutions in a vacant area using innovative planning (example: land pooling/land reconstitution in Outer Delhi, GIFT city in Gujarat).
3. Redevelopement 50 acres: Replacement of existing built-up area and preparing a new layout plan with enhanced infrastructure by way of mixed land use (example: Kidwai Nagar in Delhi).


Pingback: Current affairs & Banking Awareness | Things you should know about AMRUT- Action plan…!!
Pingback: Current affairs & Banking Awareness | Most smart cities to come up in Uttar Pradesh, Tamil Nadu..!!
Pingback: Current affairs & Banking Awareness | Quick Bytes: Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) – Housing for All by 2022.